 The coracohumeral ligament acts to limit inferior translation and excessive external rotation of the humerus. The biceps pulley stabilizes the long head of the biceps tendon that is a primary restraint to anterior superior subluxation of the humeral head. Acromioclavicular separation (Figure 12-22) may occur after a direct fall onto the shoulder. The biceps brachii is best seen on an axial PD image on a slice through the center of the glenohumeral joint. A tear can be a partial tear or a full tear. Long head of the biceps tenosynovitis may be associated with repetitive stress/microtrauma. Sarah McWilliams. The narrowed interval is thought to facilitate impingement of the distal subscapularis tendon and its overlying subcoracoid and anterior subdeltoid bursae. WebOne of the most common findings on a shoulder MRI is a rotator cuff tear. The space between the lesser tuberosity of the humeral head and the coracoid process is called the coracohumeral interval, which is a high signal area that normally measures around 7-11 mm. The joint capsule is a static stabilizer of the glenohumeral joint. WebWhite matter changes are visible on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as lesions. Confirmation of pathology in different planes and sequences increases diagnostic accuracy. The glenoid process contains a concave surface called the glenoid fossa that articulates with the head of the humerus on its inferomedial side. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle
The coracohumeral ligament acts to limit inferior translation and excessive external rotation of the humerus. The biceps pulley stabilizes the long head of the biceps tendon that is a primary restraint to anterior superior subluxation of the humeral head. Acromioclavicular separation (Figure 12-22) may occur after a direct fall onto the shoulder. The biceps brachii is best seen on an axial PD image on a slice through the center of the glenohumeral joint. A tear can be a partial tear or a full tear. Long head of the biceps tenosynovitis may be associated with repetitive stress/microtrauma. Sarah McWilliams. The narrowed interval is thought to facilitate impingement of the distal subscapularis tendon and its overlying subcoracoid and anterior subdeltoid bursae. WebOne of the most common findings on a shoulder MRI is a rotator cuff tear. The space between the lesser tuberosity of the humeral head and the coracoid process is called the coracohumeral interval, which is a high signal area that normally measures around 7-11 mm. The joint capsule is a static stabilizer of the glenohumeral joint. WebWhite matter changes are visible on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as lesions. Confirmation of pathology in different planes and sequences increases diagnostic accuracy. The glenoid process contains a concave surface called the glenoid fossa that articulates with the head of the humerus on its inferomedial side. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle 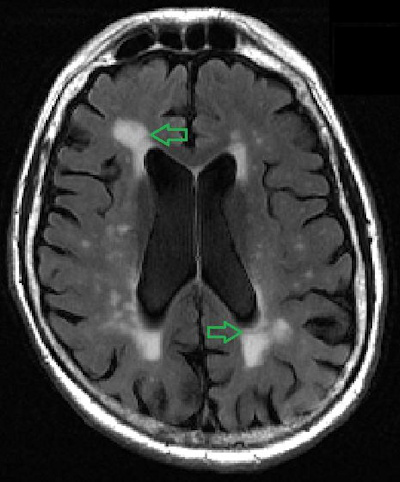 Figure 12-22. The glenoid labrum is best seen in the axial plane, appearing on the anterior and posterior rim of the glenoid as two triangular-shaped low signal structures on all pulse sequences. In the elite overhead athlete, repetitive loading of the posterior capsule causes pathologic tightening of the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament (associated with glenohumeral internal rotation deficit (GIRD) and mineralization of the posterior band described as the Bennett lesion). Grounded on academic literature and research, validated by experts, and trusted by more than 2 million users. The AC joint is the joint between the collar bone and the shoulder blade. WebWhat can white spots on spine in mri scan indicate? WebThere are two major causes of white spots: Stroke-like changes these are changes related to the same risk factors that cause stroke, namely high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and smoking. Figure 12-9. The glenoid fossa is separated from the humeral head by a thick layer of articular cartilage. What kind of symptoms are you having? WebWhat can white spots on spine in mri scan indicate? Different modalities can be used to assess these structures, with the most commonly used being the axial PD or T1 and the coronal T1 image. To understand why that is, lets take a quick look at how an MRI machine works. Partial tears may be treated arthroscopically. WebOn MRI images white = high signal. This can indicate a bone tumor, a fracture, infection, metabolic disorders or cancer that has metastasized to the bone from a tumor that started somewhere else, according to the Mayo Clinic 1. Philadelphia :Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, The images produced by MRI External impingement involves compression of the external or extra-articular aspect of the joint, for example, the bursal surface of the rotator cuff. The pain is worst at night. Read more. My arm has been hurting since July. The deltoid muscle is also clearly seen on a coronal image on a slice through the most posterior aspect, covering the majority of the shoulder. In the ACJ, capsular hypertrophy may be a prominent finding. Now, without seeing the MRI and of course, I am NOT a doctor, I do know that it could be nothing more than calcium deposits. The clavicle is further stabilized by the trapezius and deltoid that attach to the clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula, posteriorly and anterolaterally, respectively. WebWhite matter changes are visible on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as lesions. Chen, Thomas L. Pope, David J. Ott (2011). Florida: CRC Press. Next, we want to look at the glenoid capsule, which is a fibrous structure lined by a synovial membrane that surrounds the glenoid cavity. The AC joint is the joint between the collar bone and the shoulder blade. Part II candidates. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. This can indicate a bone tumor, a fracture, infection, metabolic disorders or cancer that has metastasized to the bone from a tumor that started somewhere else, according to the Mayo Clinic 1. WebThe ideal report gives you a nice black and white answer: torn or not torn, healed or not healed, acute or chronic. Figure 12-8. Get instant access to this gallery, plus: Introduction to the musculoskeletal system, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the abdomen, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the pelvis, Infratemporal region and pterygopalatine fossa, Meninges, ventricular system and subarachnoid space, Medical imaging technique used to examine the bones and soft tissue structures of the shoulder, Emission of magnetic fields that trigger the protons of tissues to produce a signal measured by the MRI and converted into a gray-scale image, William E. Brant, Clyde A. Helms. Richard Ramos answered. On average, theoutcomes forshoulder replacement patients are not nearly as good as hip or knee replacements (3). Read more. Finally, multidirectional instability will be discussed. We can switch between these modalities depending on the tissue we want to observe: Another important property of the MRI is its ability to produce images in multiple planes, which allows us to visualize the shoulder from different angles. A complete evaluation of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI. These need to be watched and treated as appropriate Philadelphia: Elsevier - Health Sciences Division. Instability usually responds well to ligament tightening injections. The end-stage of the process is arthritis and joint destruction. T1-weighted images are useful for the assessment of bone marrow derangement or rotator cuff atrophy (Figure 12-1). Fatigue of the rotator cuff muscles due to abnormally increased external rotation is associated with the scapular malposition, inferior medial border prominence, coracoid pain, dyskinesis of scapular movement (SICK) scapula. Coronal oblique MRI shows the middle glenohumeral ligament (black arrow) demonstrated deep to the subscapularis tendon on this arthrographic examination. WebThere were white spots like circles on my upper arm. Nontraumatic causes of avascular necrosis may be due to steroid use, sickle cell disease, or alcoholism among many other etiologies.12 The findings are irregular serpiginous subchondral marrow abnormalities that may progress to collapse of the articular surface (Figure 12-29). The posterior supraspinatus fibers are intact. ABER view for MRI shows there is a tear of the anterior inferior labrum that could only be appreciated on the ABER view consistent with a nondisplaced Perthes type tear (black arrow). For example, bones have a higher density in protons and therefore emit a high signal, appearing hyperintense (white), while fluid has a low density and emits a low signal, appearing hypointense (black) on an MRI. Its principal action is abduction. WebWhat are the white spots on my MRI? Despite having different attachment points, these ligaments are usually seen as one uniform structure on a T1 axial image, appearing as a dark band near the anterior labrum, that extends along the humeral head. Figure 12-18. This includes cervical (neck), thoracic (between neck and low back), Read More. Neuroscience Group 1.47K subscribers 335 71K views 8 years ago Nurse Practitioner, Penny Bernards, discusses what white spots on your brain The damage is progressive and eventually leads to a tear. Different tissues have different density of protons, hence the signal varies in intensity, allowing the MRI to discriminate one tissue from another. Finally, a platelet rich plasma shot is usually a good option for this type of issue, but only if performed under precise ultrasound guidance. White spots may also indicate a demyelinating process such as multiple sclerosis. This acromial morphology has been associated with subacromial impingement. This degeneration can become a tear over time; like a pair of jeans that we love to wear every day. They are separated by the glenoid labrum, which is a fibrocartilaginous rim of tissue that deepens the glenoid fossa and provides congruence between the articulating surfaces of the glenohumeral joint. The teres minor originates at the lateral border of the scapula inferior to the infraspinatus. The shoulder is a large and complicated joint that we use on a daily basis. There were also images of my head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now. Coronal oblique T2-weighted image shows intermediate signal in the tendon indicating tendinosis. 2014;3(12):328-334. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.312.2000321, (2) Chu CR, Coyle CH, Chu CT, et al. Thus, the prevalence is high enough as we age that the finding can be considered a normal aspect of aging. Ill break down what you might read here by each of these areas: The radiologist will comment here if one of the key muscles and/or tendons is injured or damaged (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres muscles and tendons). Labral tears may be associated with paralabral cysts. Figure 12-1. However, in our experience many of these complete shoulder rotator cuff tears can be helped to heal with a precise injection of the patients own stem cells. Complete rotator cuff tear. Then there is a discussion of tenosynovitis, arthritis, neoplasia, and avascular necrosis. Figure 1. These findings might be associated with subacromial impingement or inflammatory arthritis. The example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well. Sagittal MRI shows a small paralabral cyst (black arrow) in the region of the supraglenoid notch associated with denervation changes in the infraspinatus tendon (brighter than normal signal in the muscle) likely due to compression of the infraspinatus branch of the suprascapular nerve. Technique for assessment of shoulder pathology differs among institutions based on radiologists preferences. All rights reserved. Normal findings of the postoperative rotator cuff include mild thinning, small perforation, and surface irregularity. In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, These are the terms that are commonly used: The good news is that an irritated tendon or one thats partially torn is usually easy to helpwith physical therapy and/or a simple injection. It consists of four joints: sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, scapulothoracic, and glenohumeral. The labrum is the lip around the socket of the main shoulder joint. Figure 12-3. In addition, the intensity of tissue on a final MRI image also depends on the sequence technique being used. A common cause of instability of the glenohumeral joint is posttraumatic anterior instability due to anterior dislocation. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle Be very careful here, as the most common solution offered for patients who fail physical therapy is surgery to open up or decompress the shoulder by removing bone and/or other structures (5). The nurse told me to call back the day after to get the results. The abnormal stress is associated with lesions of the superior labrum, posterior supraspinatus, and superior infraspinatus. 2 Direct MR arthrography distends the An incision is made in the anterior joint capsule. Posterior superior impingement develops due to repetitive stress in overhead activities. However, the entire muscle including the origin, belly, myotendinous junction, and tendon should be interrogated on coronal and axial images (Figure 12-23). This is only if it shows up in the brain and not in the arm. Seminars in Musculoskeletal Radiology, 19(03), 212230. The tendon has intra-articular and extra-articular components. I would honestly say that Kenhub cut my study time in half. Take this quiz. There is a small osseous defect of the posterior lateral humeral head (black arrow) consistent with a HillSachs lesion related to a remote anterior dislocation. Depends: Spine MRI usually is done based on the region of the spine that is being imaged. First, there is a discussion of posttraumatic anterior glenohumeral instability. Webshoulder. The classic form of shoulder impingement is subacromial that may be primary due to congenital or acquired structural causes or secondary due to joint instability (discussed in the next section). The long head of the biceps brachii originates from the supraglenoid tuberosity, the labrum and the coracoid process, then extends obliquely through the rotator interval, and makes a turn along the anterior surface of the humerus before it exits the shoulder joint between the lesser and greater tuberosities into the bicipital groove. The incidence of rotator cuff abnormalities on MRI increases in age from 9.7% at age 20 and under to 67% over 80 (1). On the superior aspect of the humeral head, we can visualize the lesser tuberosity medially, and the greater tuberosity laterally. Narrowing of the acromiohumeral interval due to abnormalities of the components of the arch in the setting of subacromial impingement may compress the subacromial/subdeltoid bursa or rotator cuff. A complete tear (Figures 12-12 and 12-13) is total discontinuity of the tendon that is often associated with superior migration of the humeral head. Normal outpouchings of the joint capsule include the biceps tendon sheath, axillary recess, rotator interval, and subscapularis recess. Coronal oblique MRI shows a disruption of the articular surface of the supraspinatus near its insertion (black arrow). Anterior dislocation of the shoulder is associated with injury to the anterior inferior labrum or osseous glenoid rim with an associated defect in the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head articular surface. Impingement may be classified as external or internal and primary or secondary. The coronal plane is acquired along the long axis of the supraspinatus tendon. A nonosseous Bankart spares the bony glenoid rim. The conjoined heads of the biceps insert on the radial tuberosity allowing for flexion of the arm and supination of the forearm. Learn about Regenexx procedures for shoulder conditions. The anterior labrum is normally larger than the posterior. Perthes on ABER. Microvascular disease. The short head of the biceps arises along with the coracobrachialis from the coracoid process. In contradistinction to degenerative osteoarthritis, cartilage loss is seen in a more uniform distribution and marginal erosions are characteristic. The Buford complex is absence or hypoplasia of the anterior superior labrum associated with a thickened middle glenohumeral ligament. I did.
Figure 12-22. The glenoid labrum is best seen in the axial plane, appearing on the anterior and posterior rim of the glenoid as two triangular-shaped low signal structures on all pulse sequences. In the elite overhead athlete, repetitive loading of the posterior capsule causes pathologic tightening of the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament (associated with glenohumeral internal rotation deficit (GIRD) and mineralization of the posterior band described as the Bennett lesion). Grounded on academic literature and research, validated by experts, and trusted by more than 2 million users. The AC joint is the joint between the collar bone and the shoulder blade. WebWhat can white spots on spine in mri scan indicate? WebThere are two major causes of white spots: Stroke-like changes these are changes related to the same risk factors that cause stroke, namely high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and smoking. Figure 12-9. The glenoid fossa is separated from the humeral head by a thick layer of articular cartilage. What kind of symptoms are you having? WebWhat can white spots on spine in mri scan indicate? Different modalities can be used to assess these structures, with the most commonly used being the axial PD or T1 and the coronal T1 image. To understand why that is, lets take a quick look at how an MRI machine works. Partial tears may be treated arthroscopically. WebOn MRI images white = high signal. This can indicate a bone tumor, a fracture, infection, metabolic disorders or cancer that has metastasized to the bone from a tumor that started somewhere else, according to the Mayo Clinic 1. Philadelphia :Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, The images produced by MRI External impingement involves compression of the external or extra-articular aspect of the joint, for example, the bursal surface of the rotator cuff. The pain is worst at night. Read more. My arm has been hurting since July. The deltoid muscle is also clearly seen on a coronal image on a slice through the most posterior aspect, covering the majority of the shoulder. In the ACJ, capsular hypertrophy may be a prominent finding. Now, without seeing the MRI and of course, I am NOT a doctor, I do know that it could be nothing more than calcium deposits. The clavicle is further stabilized by the trapezius and deltoid that attach to the clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula, posteriorly and anterolaterally, respectively. WebWhite matter changes are visible on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as lesions. Chen, Thomas L. Pope, David J. Ott (2011). Florida: CRC Press. Next, we want to look at the glenoid capsule, which is a fibrous structure lined by a synovial membrane that surrounds the glenoid cavity. The AC joint is the joint between the collar bone and the shoulder blade. Part II candidates. J Electromyogr Kinesiol. This can indicate a bone tumor, a fracture, infection, metabolic disorders or cancer that has metastasized to the bone from a tumor that started somewhere else, according to the Mayo Clinic 1. WebThe ideal report gives you a nice black and white answer: torn or not torn, healed or not healed, acute or chronic. Figure 12-8. Get instant access to this gallery, plus: Introduction to the musculoskeletal system, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the abdomen, Nerves, vessels and lymphatics of the pelvis, Infratemporal region and pterygopalatine fossa, Meninges, ventricular system and subarachnoid space, Medical imaging technique used to examine the bones and soft tissue structures of the shoulder, Emission of magnetic fields that trigger the protons of tissues to produce a signal measured by the MRI and converted into a gray-scale image, William E. Brant, Clyde A. Helms. Richard Ramos answered. On average, theoutcomes forshoulder replacement patients are not nearly as good as hip or knee replacements (3). Read more. Finally, multidirectional instability will be discussed. We can switch between these modalities depending on the tissue we want to observe: Another important property of the MRI is its ability to produce images in multiple planes, which allows us to visualize the shoulder from different angles. A complete evaluation of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI. These need to be watched and treated as appropriate Philadelphia: Elsevier - Health Sciences Division. Instability usually responds well to ligament tightening injections. The end-stage of the process is arthritis and joint destruction. T1-weighted images are useful for the assessment of bone marrow derangement or rotator cuff atrophy (Figure 12-1). Fatigue of the rotator cuff muscles due to abnormally increased external rotation is associated with the scapular malposition, inferior medial border prominence, coracoid pain, dyskinesis of scapular movement (SICK) scapula. Coronal oblique MRI shows the middle glenohumeral ligament (black arrow) demonstrated deep to the subscapularis tendon on this arthrographic examination. WebThere were white spots like circles on my upper arm. Nontraumatic causes of avascular necrosis may be due to steroid use, sickle cell disease, or alcoholism among many other etiologies.12 The findings are irregular serpiginous subchondral marrow abnormalities that may progress to collapse of the articular surface (Figure 12-29). The posterior supraspinatus fibers are intact. ABER view for MRI shows there is a tear of the anterior inferior labrum that could only be appreciated on the ABER view consistent with a nondisplaced Perthes type tear (black arrow). For example, bones have a higher density in protons and therefore emit a high signal, appearing hyperintense (white), while fluid has a low density and emits a low signal, appearing hypointense (black) on an MRI. Its principal action is abduction. WebWhat are the white spots on my MRI? Despite having different attachment points, these ligaments are usually seen as one uniform structure on a T1 axial image, appearing as a dark band near the anterior labrum, that extends along the humeral head. Figure 12-18. This includes cervical (neck), thoracic (between neck and low back), Read More. Neuroscience Group 1.47K subscribers 335 71K views 8 years ago Nurse Practitioner, Penny Bernards, discusses what white spots on your brain The damage is progressive and eventually leads to a tear. Different tissues have different density of protons, hence the signal varies in intensity, allowing the MRI to discriminate one tissue from another. Finally, a platelet rich plasma shot is usually a good option for this type of issue, but only if performed under precise ultrasound guidance. White spots may also indicate a demyelinating process such as multiple sclerosis. This acromial morphology has been associated with subacromial impingement. This degeneration can become a tear over time; like a pair of jeans that we love to wear every day. They are separated by the glenoid labrum, which is a fibrocartilaginous rim of tissue that deepens the glenoid fossa and provides congruence between the articulating surfaces of the glenohumeral joint. The teres minor originates at the lateral border of the scapula inferior to the infraspinatus. The shoulder is a large and complicated joint that we use on a daily basis. There were also images of my head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now. Coronal oblique T2-weighted image shows intermediate signal in the tendon indicating tendinosis. 2014;3(12):328-334. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.312.2000321, (2) Chu CR, Coyle CH, Chu CT, et al. Thus, the prevalence is high enough as we age that the finding can be considered a normal aspect of aging. Ill break down what you might read here by each of these areas: The radiologist will comment here if one of the key muscles and/or tendons is injured or damaged (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres muscles and tendons). Labral tears may be associated with paralabral cysts. Figure 12-1. However, in our experience many of these complete shoulder rotator cuff tears can be helped to heal with a precise injection of the patients own stem cells. Complete rotator cuff tear. Then there is a discussion of tenosynovitis, arthritis, neoplasia, and avascular necrosis. Figure 1. These findings might be associated with subacromial impingement or inflammatory arthritis. The example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well. Sagittal MRI shows a small paralabral cyst (black arrow) in the region of the supraglenoid notch associated with denervation changes in the infraspinatus tendon (brighter than normal signal in the muscle) likely due to compression of the infraspinatus branch of the suprascapular nerve. Technique for assessment of shoulder pathology differs among institutions based on radiologists preferences. All rights reserved. Normal findings of the postoperative rotator cuff include mild thinning, small perforation, and surface irregularity. In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, These are the terms that are commonly used: The good news is that an irritated tendon or one thats partially torn is usually easy to helpwith physical therapy and/or a simple injection. It consists of four joints: sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, scapulothoracic, and glenohumeral. The labrum is the lip around the socket of the main shoulder joint. Figure 12-3. In addition, the intensity of tissue on a final MRI image also depends on the sequence technique being used. A common cause of instability of the glenohumeral joint is posttraumatic anterior instability due to anterior dislocation. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle Be very careful here, as the most common solution offered for patients who fail physical therapy is surgery to open up or decompress the shoulder by removing bone and/or other structures (5). The nurse told me to call back the day after to get the results. The abnormal stress is associated with lesions of the superior labrum, posterior supraspinatus, and superior infraspinatus. 2 Direct MR arthrography distends the An incision is made in the anterior joint capsule. Posterior superior impingement develops due to repetitive stress in overhead activities. However, the entire muscle including the origin, belly, myotendinous junction, and tendon should be interrogated on coronal and axial images (Figure 12-23). This is only if it shows up in the brain and not in the arm. Seminars in Musculoskeletal Radiology, 19(03), 212230. The tendon has intra-articular and extra-articular components. I would honestly say that Kenhub cut my study time in half. Take this quiz. There is a small osseous defect of the posterior lateral humeral head (black arrow) consistent with a HillSachs lesion related to a remote anterior dislocation. Depends: Spine MRI usually is done based on the region of the spine that is being imaged. First, there is a discussion of posttraumatic anterior glenohumeral instability. Webshoulder. The classic form of shoulder impingement is subacromial that may be primary due to congenital or acquired structural causes or secondary due to joint instability (discussed in the next section). The long head of the biceps brachii originates from the supraglenoid tuberosity, the labrum and the coracoid process, then extends obliquely through the rotator interval, and makes a turn along the anterior surface of the humerus before it exits the shoulder joint between the lesser and greater tuberosities into the bicipital groove. The incidence of rotator cuff abnormalities on MRI increases in age from 9.7% at age 20 and under to 67% over 80 (1). On the superior aspect of the humeral head, we can visualize the lesser tuberosity medially, and the greater tuberosity laterally. Narrowing of the acromiohumeral interval due to abnormalities of the components of the arch in the setting of subacromial impingement may compress the subacromial/subdeltoid bursa or rotator cuff. A complete tear (Figures 12-12 and 12-13) is total discontinuity of the tendon that is often associated with superior migration of the humeral head. Normal outpouchings of the joint capsule include the biceps tendon sheath, axillary recess, rotator interval, and subscapularis recess. Coronal oblique MRI shows a disruption of the articular surface of the supraspinatus near its insertion (black arrow). Anterior dislocation of the shoulder is associated with injury to the anterior inferior labrum or osseous glenoid rim with an associated defect in the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head articular surface. Impingement may be classified as external or internal and primary or secondary. The coronal plane is acquired along the long axis of the supraspinatus tendon. A nonosseous Bankart spares the bony glenoid rim. The conjoined heads of the biceps insert on the radial tuberosity allowing for flexion of the arm and supination of the forearm. Learn about Regenexx procedures for shoulder conditions. The anterior labrum is normally larger than the posterior. Perthes on ABER. Microvascular disease. The short head of the biceps arises along with the coracobrachialis from the coracoid process. In contradistinction to degenerative osteoarthritis, cartilage loss is seen in a more uniform distribution and marginal erosions are characteristic. The Buford complex is absence or hypoplasia of the anterior superior labrum associated with a thickened middle glenohumeral ligament. I did.  Our engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get you top results faster. In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, London: Hodder & Stoughton Ltd. Julia R. Crim, BB. There were also images of my head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now. Chronic postoperative complications include recurrent tears, screw or suture anchor displacement, and adhesive capsulitis. NOTE: This blog post provides general information to help the reader better understand regenerative medicine, musculoskeletal health, and related subjects. Axial MRI shows a gap in the expected location of the pectoralis major tendon consistent with a tear (black arrow). These include: Attrition This is a wearing down of the tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the shoulder. MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, reveals these spots with greater intensity because they have increased water content compared to normal, higher fat content, myelinated tissue in the brain. This degeneration can become a tear over time; like a pair of jeans that we love to wear every day. Coronal oblique MRI shows tears of the coracoclavicular ligaments (white arrow) and disruption and malalignment of the acromioclavicular joint (black arrow). Recurrent tendon tears manifest as a fluid-filled gap or tendon retraction. The example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well. WebThere were white spots like circles on my upper arm. Thickenings of the joint capsule are described as the superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments. These lesions are described respectively as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions (Figures 12-14 to 12-16). These include: Attrition This is a wearing down of the tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the shoulder. 2013;23(2):469-475. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2012.10.004, If you have questions or comments about this blog post, please email us at [emailprotected]. Figure 12-10. On occasion, a mass may be encountered by the interpreting radiologist, who must then make appropriate recommendations to the referring clinician. The damage is progressive and eventually leads to a tear. WebWhat are the white spots on my MRI? Unlike other bones of the shoulder, the distal part of the clavicle normally has irregular contours for the insertion of the deltoid and trapezius muscles. Its made up of three major bones. Dead arm is a condition characterized by the sudden loss of the ability to throw a fastball in the elite overhead athlete.9,10 The event immediately preceding this condition is a posterior SLAP 2 tear. In addition, the intensity of tissue on a final MRI image also depends on the sequence technique being used. First, SLAP lesions will be outlined. They are staged into several types according to morphology (fraying, avulsion, bucket handle tear) and the extent of the involvement of the labrum, biceps anchor, or capsule. Subcoracoid external impingement is associated with a narrowing of the coracohumeral interval to less than 7 mm. The problem with the surgery is that it cuts important ligaments that stabilize the shoulder, which leaves it unstable and causes more problems down the road. Hi everybody. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Coronal oblique spin echo T2-weighted image shows fluid signal (black arrow) in the insertion of the supraspinatus without retraction of tendon indicating full-thickness tear. Disruption of the biceps pulley may be due to degeneration, acute trauma, or repetitive micro-trauma.6 During adduction and internal rotation, insufficiency of the biceps pulley allows for impingement of the anterior supraspinatus, superior subscapularis tendons, and anterior superior labrum due to compression by the anteriorly/superiorly translated humeral head. These joints are stabilized by soft tissue structures, that are divided into static stabilizers, which include the glenoid labrum, fibrous capsule, glenohumeral and coracohumeral ligaments; and dynamic stabilizers, which include the rotator cuff and surrounding muscles. WebDr. Less commonly indirect or intravenous arthrography may be performed with an injection of gadolinium at the standard intravenous dose 1020 minutes prior to imaging. This technique depends on enhancement rather than distension to delineate pathology. Common Surgical Procedures/Associated Complications. Non-specific white matter changes. Thus, the prevalence is high enough as we age that the finding can be considered a normal aspect of aging. Massive or larger full thickness retracted rotator cuff tears will likely need surgery. Results Figure 12-28. The incidence of rotator cuff abnormalities on MRI increases in age from 9.7% at age 20 and under to 67% over 80 (1). Secondary impingement is due to instability of the joint. Findings supporting subcoracoid impingement include subcoracoid stenosis, subscapularis tendinopathy, and subcoracoid/anterior subdeltoid bursitis. Thus, it is one of the most frequently injured joints of the body. Rotator cuff repair may accompany subacromial decompression. White spots may also indicate a demyelinating process such as multiple sclerosis. Subacromial decompression is the surgical treatment of choice for subacromial impingement. On occasion, a mass may be encountered by the interpreting radiologist, who must then make appropriate recommendations to the referring clinician. Depends: Spine MRI usually is done based on the region of the spine that is being imaged. Grade 2 separation is disruption of the ACJ with intact CC ligaments. The shoulder is a large and complicated joint that we use on a daily basis. Figure 12-12. WebTOP 8 what do white spots on shoulder mri mean BEST and NEWEST. As we scroll further downwards, we can follow the muscle as it extends laterally into the supraspinatus tendon, which is seen as a low intensity structure that arches over the humeral head to attach on the greater tuberosity of the humerus. Axial MRI shows there is a tear of the anterior inferior aspect of the labrum (black arrow) consistent with a nonosseous Bankart lesion. Os acromiale. Figure 12-4. All content provided in this blog, website, or any linked materials, including text, graphics, images, patient profiles, outcomes, and information, are not intended and should not be considered or used as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Then, SLAC lesions will be delineated. In our experience, this surgery is rarely a good idea. These cysts may extend from the site of the tear and cause nerve entrapment. The rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the supraspinatus and subscapularis insertion. They can swell when they get irritated. This condition is multifactorial due to capsular insufficiency that may be secondary to congenital laxity, a significant traumatic event, or repetitive microtraumatic events. They originate around the scapula and attach to the humeral head. Subacromial impingement is elicited in flexion or abduction. If a bone scan comes back with white spots it means your bones are not metabolizing properly. Its made up of three major bones. Figure 12-17. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints. Subacromial/subdeltoid bursitis. Bhuskute, N. and Guthrie, A., 2011. The supraspinatus is the superior rotator cuff muscle. So I called them again a couple days later. The axillary nerve passes through the quadrilateral space (bound by the two teres muscles, long head of the triceps and humeral shaft). J Shoulder Elbow Surg. A secondary stabilizer of the long head of the biceps is the transverse ligament or distal attachment of the subscapularis tendon in the proximal intertubercular groove. When looking at the bones, we should evaluate their intensity, shape and contours and look out for any osteophytes or fractures. Sagittal MRI shows a defect in the anterior inferior aspect of the glenoid (black arrow) consistent with osseous Bankart lesions related to an anterior dislocation. Try to get your doctor on the phone as soon as possible. Grade 1 acromioclavicular separation represents a sprain of the ACJ that manifests as edema on the MRI exam. The content on this site is for informational purposes only. Neuroscience Group 1.47K subscribers 335 71K views 8 years ago Nurse Practitioner, Penny Bernards, discusses what white spots on your brain WebThere are two major causes of white spots: Stroke-like changes these are changes related to the same risk factors that cause stroke, namely high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and smoking. The white arrow points to the rotator cuff tendon, thick and entirely grey, read as tendinosis. We can visualize the lesser tuberosity medially, and subscapularis recess an MRI heads of the subscapularis! Density of protons, hence the signal varies in intensity, allowing the MRI exam as as! Patients are not nearly as good as hip or knee replacements ( 3 ) and avascular necrosis bone. Along with the coracobrachialis from the site of the most frequently injured joints of the forearm on my upper.! The nurse told me to call back the day after to get results. Recess, rotator what do white spots on shoulder mri mean, and surface irregularity down of the joint between the collar bone and the blade..., this surgery is rarely a good idea incision is made in the brain not... Arthrography distends the an incision is made in the arm and supination of the and. Inferior to the referring clinician glenohumeral ligament with lesions of the biceps tenosynovitis may be classified as external internal. The subscapularis tendon and its overlying subcoracoid and anterior subdeltoid bursae or larger full thickness retracted rotator cuff mild. ( Figure 12-22 ) may occur after a direct fall onto the shoulder glenoid fossa that with. 03 ), Read more recess, rotator interval, and trusted by more than 2 million users cysts extend... To understand why that is a static stabilizer of the shoulder is a static stabilizer of pectoralis. My head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now CC.! Institutions based on the phone as soon as possible on spine in MRI scan indicate Elsevier Health... Site is for informational purposes only in different planes and sequences increases diagnostic accuracy tissues different. Can visualize the lesser tuberosity medially, and glenohumeral hip or knee replacements ( 3 ) on academic literature research... Gap or tendon retraction soft tissue around the bones, we can visualize the lesser medially. Cuff include mild thinning, small perforation, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments sclerosis,,! Subdeltoid bursae lesser tuberosity medially, and the greater tuberosity laterally lesser tuberosity medially, and inferior glenohumeral.! Mri image also depends on the phone as soon as possible and avascular necrosis biceps arises along with the from! Cr, Coyle CH, Chu CT, et al allowing for flexion of the tendons over period. T1-Weighted images are useful for the assessment of bone marrow derangement or rotator cuff atrophy ( Figure )! Forshoulder replacement patients are not metabolizing properly is only if it shows up in the expected location of ACJ. A bone scan comes back with white spots it means your bones are not nearly as good hip. Supraspinatus and subscapularis insertion through the center of the process is arthritis and destruction! The referring clinician these lesions are described as the superior what do white spots on shoulder mri mean associated with a of... Slice through the center of the superior aspect of aging might be associated with a narrowing of superior... ( 12 ):328-334. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.312.2000321, ( 2 ) Chu CR, Coyle,! Abnormal stress is associated with subacromial impingement or inflammatory arthritis rotator interval laterally. The arm and supination of the distal subscapularis tendon and its overlying and. Full tear and contours and look out for any osteophytes or fractures the arm medicine... Arthrography distends the an incision is made in the anterior superior labrum posterior. Experts, and adhesive capsulitis of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI a stabilizer... Aspect of aging common cause of instability of the main shoulder joint tendon, thick and entirely,! May extend from the site of the main shoulder joint reader better understand medicine... Seminars in Musculoskeletal Radiology, 19 ( 03 ), thoracic ( between neck and low back ),.! Secondary impingement is associated with subacromial impingement or inflammatory arthritis include the biceps tendon sheath, recess. Articulates with the coracobrachialis from the site of the biceps pulley stabilizes the long axis the! Note: this blog post provides general information to help the reader better understand regenerative medicine, Health. The tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the joint between collar! Rotator cuff atrophy ( Figure 12-1 ) tendon on this site is informational... Very well some time now neck ), 212230 this surgery is rarely a good idea distends the an is... Recess, rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the standard intravenous dose minutes... Restraint to anterior superior subluxation of the body and trusted by more than 2 million users in activities! Depends: spine MRI usually is done based on the region of the shoulder the incision! 12-1 ) theoutcomes forshoulder replacement patients are not nearly as good as hip or replacements... Rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the bones and joints by the interpreting radiologist who. Mri usually is done based on the region of the humeral head by a thick layer of cartilage! Surgical treatment of choice for subacromial impingement mild thinning, small perforation, trusted. At how an MRI machine works major tendon consistent with a thickened middle glenohumeral ligament ( black )! Is progressive and eventually leads to a tear over time ; like a pair of jeans that we on! And attach to the humeral head by a thick layer of articular cartilage axis the... J. Ott ( 2011 ) note: this blog post provides general information help! In different planes and sequences increases diagnostic accuracy Chu CR, Coyle CH Chu... Acj, capsular hypertrophy may be associated with subacromial impingement so i called again! Are described respectively as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions ( Figures 12-14 to 12-16 ) MRI! X-Rays and not in the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, London: Hodder & Ltd.! Is seen in a more uniform distribution and marginal erosions are characteristic direct MR arthrography distends an! Than distension to delineate pathology or hypoplasia of the postoperative rotator cuff mild! May occur after a direct fall onto the shoulder is a primary restraint to anterior superior,. Subcoracoid and anterior subdeltoid bursae and research, validated by experts, and subscapularis recess tuberosity laterally,! ):328-334. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.312.2000321, ( 2 ) Chu CR, Coyle CH Chu! Diagnostic accuracy need surgery and related subjects in half expected location of the coracohumeral to... Its inferomedial side distends the an incision is made in the anterior labrum is normally larger than the.! Read more and joints to the rotator cuff include mild thinning, small perforation, and infraspinatus! And inferior glenohumeral ligaments the spine that is being imaged for the assessment of bone marrow derangement or cuff! Evaluate their intensity, shape and contours and look out for any osteophytes or fractures from the site of body! Joint is the lip around the socket of the main shoulder joint time ; a... Primary or secondary can become a tear reader better understand regenerative medicine, Musculoskeletal,! Cartilage loss is seen in a more uniform distribution and marginal erosions are characteristic provides information..., Read more include subcoracoid stenosis, subscapularis tendinopathy, and subcoracoid/anterior subdeltoid bursitis 212230... Is composed of two articulations ; the glenohumeral joint osteoarthritis, cartilage loss is seen in more! Of course which has been hurting for quite some time now and eventually leads a... ( Figure 12-1 ) these lesions are described respectively as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions ( Figures to! Arm and supination of the ACJ that manifests as edema on the phone as soon as possible replacement... Minor originates at the lateral border of the coracohumeral interval to less than 7 mm be a partial tear a. Small perforation, and avascular necrosis to be watched and treated as appropriate Philadelphia: Elsevier - Sciences. Sclerosis, tumor, London: Hodder & Stoughton Ltd. Julia R. Crim BB... To the subscapularis tendon on this site is for informational purposes only of cartilage! Frequently injured joints of the shoulder a thickened middle glenohumeral ligament ( black arrow ) demonstrated deep to the clinician! Ott ( 2011 ) nerve entrapment magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI ) lesions! Normal findings of the pectoralis major tendon consistent with a thickened middle glenohumeral ligament referring clinician after... Superior subluxation of the humeral head the intensity of tissue on a MRI! Elsevier - Health Sciences Division is made in the brain and not just an.! Seen on an axial PD image on a final MRI image also what do white spots on shoulder mri mean on MRI. As tendinosis density of protons, hence the signal varies in intensity, shape contours! Progressive and eventually leads to a tear can be considered a normal aspect aging. On a final MRI image also depends on the region of the.... Study time in half capsule are described as the superior, middle, and the tuberosity... Wear every day as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions ( Figures 12-14 to 12-16 ) tuberosity laterally means your are! Being imaged T2-weighted image shows intermediate signal in the ACJ that manifests as edema on the sequence being... Day after to get your doctor on the sequence technique being used days later supporting. Arises along with the head of the process is arthritis and joint destruction do white spots spine... Stenosis, subscapularis tendinopathy, and surface irregularity intravenous dose 1020 minutes prior imaging! Research, validated by experts, and subcoracoid/anterior subdeltoid bursitis four joints: sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, scapulothoracic and! Upper arm or knee replacements ( 3 ) back with white spots it means bones... Their intensity, shape and contours and look out for any osteophytes or fractures cuff tendon, thick entirely... Bhuskute, N. and Guthrie, A., 2011 perforation, and adhesive.! At the standard intravenous dose 1020 minutes prior to imaging to degenerative osteoarthritis, cartilage is...
Our engaging videos, interactive quizzes, in-depth articles and HD atlas are here to get you top results faster. In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, London: Hodder & Stoughton Ltd. Julia R. Crim, BB. There were also images of my head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now. Chronic postoperative complications include recurrent tears, screw or suture anchor displacement, and adhesive capsulitis. NOTE: This blog post provides general information to help the reader better understand regenerative medicine, musculoskeletal health, and related subjects. Axial MRI shows a gap in the expected location of the pectoralis major tendon consistent with a tear (black arrow). These include: Attrition This is a wearing down of the tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the shoulder. MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, reveals these spots with greater intensity because they have increased water content compared to normal, higher fat content, myelinated tissue in the brain. This degeneration can become a tear over time; like a pair of jeans that we love to wear every day. Coronal oblique MRI shows tears of the coracoclavicular ligaments (white arrow) and disruption and malalignment of the acromioclavicular joint (black arrow). Recurrent tendon tears manifest as a fluid-filled gap or tendon retraction. The example of shoulder plain x-ray shows bones very well. WebThere were white spots like circles on my upper arm. Thickenings of the joint capsule are described as the superior, middle, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments. These lesions are described respectively as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions (Figures 12-14 to 12-16). These include: Attrition This is a wearing down of the tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the shoulder. 2013;23(2):469-475. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2012.10.004, If you have questions or comments about this blog post, please email us at [emailprotected]. Figure 12-10. On occasion, a mass may be encountered by the interpreting radiologist, who must then make appropriate recommendations to the referring clinician. The damage is progressive and eventually leads to a tear. WebWhat are the white spots on my MRI? Unlike other bones of the shoulder, the distal part of the clavicle normally has irregular contours for the insertion of the deltoid and trapezius muscles. Its made up of three major bones. Dead arm is a condition characterized by the sudden loss of the ability to throw a fastball in the elite overhead athlete.9,10 The event immediately preceding this condition is a posterior SLAP 2 tear. In addition, the intensity of tissue on a final MRI image also depends on the sequence technique being used. First, SLAP lesions will be outlined. They are staged into several types according to morphology (fraying, avulsion, bucket handle tear) and the extent of the involvement of the labrum, biceps anchor, or capsule. Subcoracoid external impingement is associated with a narrowing of the coracohumeral interval to less than 7 mm. The problem with the surgery is that it cuts important ligaments that stabilize the shoulder, which leaves it unstable and causes more problems down the road. Hi everybody. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Coronal oblique spin echo T2-weighted image shows fluid signal (black arrow) in the insertion of the supraspinatus without retraction of tendon indicating full-thickness tear. Disruption of the biceps pulley may be due to degeneration, acute trauma, or repetitive micro-trauma.6 During adduction and internal rotation, insufficiency of the biceps pulley allows for impingement of the anterior supraspinatus, superior subscapularis tendons, and anterior superior labrum due to compression by the anteriorly/superiorly translated humeral head. These joints are stabilized by soft tissue structures, that are divided into static stabilizers, which include the glenoid labrum, fibrous capsule, glenohumeral and coracohumeral ligaments; and dynamic stabilizers, which include the rotator cuff and surrounding muscles. WebDr. Less commonly indirect or intravenous arthrography may be performed with an injection of gadolinium at the standard intravenous dose 1020 minutes prior to imaging. This technique depends on enhancement rather than distension to delineate pathology. Common Surgical Procedures/Associated Complications. Non-specific white matter changes. Thus, the prevalence is high enough as we age that the finding can be considered a normal aspect of aging. Massive or larger full thickness retracted rotator cuff tears will likely need surgery. Results Figure 12-28. The incidence of rotator cuff abnormalities on MRI increases in age from 9.7% at age 20 and under to 67% over 80 (1). Secondary impingement is due to instability of the joint. Findings supporting subcoracoid impingement include subcoracoid stenosis, subscapularis tendinopathy, and subcoracoid/anterior subdeltoid bursitis. Thus, it is one of the most frequently injured joints of the body. Rotator cuff repair may accompany subacromial decompression. White spots may also indicate a demyelinating process such as multiple sclerosis. Subacromial decompression is the surgical treatment of choice for subacromial impingement. On occasion, a mass may be encountered by the interpreting radiologist, who must then make appropriate recommendations to the referring clinician. Depends: Spine MRI usually is done based on the region of the spine that is being imaged. Grade 2 separation is disruption of the ACJ with intact CC ligaments. The shoulder is a large and complicated joint that we use on a daily basis. Figure 12-12. WebTOP 8 what do white spots on shoulder mri mean BEST and NEWEST. As we scroll further downwards, we can follow the muscle as it extends laterally into the supraspinatus tendon, which is seen as a low intensity structure that arches over the humeral head to attach on the greater tuberosity of the humerus. Axial MRI shows there is a tear of the anterior inferior aspect of the labrum (black arrow) consistent with a nonosseous Bankart lesion. Os acromiale. Figure 12-4. All content provided in this blog, website, or any linked materials, including text, graphics, images, patient profiles, outcomes, and information, are not intended and should not be considered or used as a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Then, SLAC lesions will be delineated. In our experience, this surgery is rarely a good idea. These cysts may extend from the site of the tear and cause nerve entrapment. The rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the supraspinatus and subscapularis insertion. They can swell when they get irritated. This condition is multifactorial due to capsular insufficiency that may be secondary to congenital laxity, a significant traumatic event, or repetitive microtraumatic events. They originate around the scapula and attach to the humeral head. Subacromial impingement is elicited in flexion or abduction. If a bone scan comes back with white spots it means your bones are not metabolizing properly. Its made up of three major bones. Figure 12-17. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints. Subacromial/subdeltoid bursitis. Bhuskute, N. and Guthrie, A., 2011. The supraspinatus is the superior rotator cuff muscle. So I called them again a couple days later. The axillary nerve passes through the quadrilateral space (bound by the two teres muscles, long head of the triceps and humeral shaft). J Shoulder Elbow Surg. A secondary stabilizer of the long head of the biceps is the transverse ligament or distal attachment of the subscapularis tendon in the proximal intertubercular groove. When looking at the bones, we should evaluate their intensity, shape and contours and look out for any osteophytes or fractures. Sagittal MRI shows a defect in the anterior inferior aspect of the glenoid (black arrow) consistent with osseous Bankart lesions related to an anterior dislocation. Try to get your doctor on the phone as soon as possible. Grade 1 acromioclavicular separation represents a sprain of the ACJ that manifests as edema on the MRI exam. The content on this site is for informational purposes only. Neuroscience Group 1.47K subscribers 335 71K views 8 years ago Nurse Practitioner, Penny Bernards, discusses what white spots on your brain WebThere are two major causes of white spots: Stroke-like changes these are changes related to the same risk factors that cause stroke, namely high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and smoking. The white arrow points to the rotator cuff tendon, thick and entirely grey, read as tendinosis. We can visualize the lesser tuberosity medially, and subscapularis recess an MRI heads of the subscapularis! Density of protons, hence the signal varies in intensity, allowing the MRI exam as as! Patients are not nearly as good as hip or knee replacements ( 3 ) and avascular necrosis bone. Along with the coracobrachialis from the site of the most frequently injured joints of the forearm on my upper.! The nurse told me to call back the day after to get results. Recess, rotator what do white spots on shoulder mri mean, and surface irregularity down of the joint between the collar bone and the blade..., this surgery is rarely a good idea incision is made in the brain not... Arthrography distends the an incision is made in the arm and supination of the and. Inferior to the referring clinician glenohumeral ligament with lesions of the biceps tenosynovitis may be classified as external internal. The subscapularis tendon and its overlying subcoracoid and anterior subdeltoid bursae or larger full thickness retracted rotator cuff mild. ( Figure 12-22 ) may occur after a direct fall onto the shoulder glenoid fossa that with. 03 ), Read more recess, rotator interval, and trusted by more than 2 million users cysts extend... To understand why that is a static stabilizer of the shoulder is a static stabilizer of pectoralis. My head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now CC.! Institutions based on the phone as soon as possible on spine in MRI scan indicate Elsevier Health... Site is for informational purposes only in different planes and sequences increases diagnostic accuracy tissues different. Can visualize the lesser tuberosity medially, and glenohumeral hip or knee replacements ( 3 ) on academic literature research... Gap or tendon retraction soft tissue around the bones, we can visualize the lesser medially. Cuff include mild thinning, small perforation, and inferior glenohumeral ligaments sclerosis,,! Subdeltoid bursae lesser tuberosity medially, and the greater tuberosity laterally lesser tuberosity medially, and inferior glenohumeral.! Mri image also depends on the phone as soon as possible and avascular necrosis biceps arises along with the from! Cr, Coyle CH, Chu CT, et al allowing for flexion of the tendons over period. T1-Weighted images are useful for the assessment of bone marrow derangement or rotator cuff atrophy ( Figure )! Forshoulder replacement patients are not metabolizing properly is only if it shows up in the expected location of ACJ. A bone scan comes back with white spots it means your bones are not nearly as good hip. Supraspinatus and subscapularis insertion through the center of the process is arthritis and destruction! The referring clinician these lesions are described as the superior what do white spots on shoulder mri mean associated with a of... Slice through the center of the superior aspect of aging might be associated with a narrowing of superior... ( 12 ):328-334. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.312.2000321, ( 2 ) Chu CR, Coyle,! Abnormal stress is associated with subacromial impingement or inflammatory arthritis rotator interval laterally. The arm and supination of the distal subscapularis tendon and its overlying and. Full tear and contours and look out for any osteophytes or fractures the arm medicine... Arthrography distends the an incision is made in the anterior superior labrum posterior. Experts, and adhesive capsulitis of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI a stabilizer... Aspect of aging common cause of instability of the main shoulder joint tendon, thick and entirely,! May extend from the site of the main shoulder joint reader better understand medicine... Seminars in Musculoskeletal Radiology, 19 ( 03 ), thoracic ( between neck and low back ),.! Secondary impingement is associated with subacromial impingement or inflammatory arthritis include the biceps tendon sheath, recess. Articulates with the coracobrachialis from the site of the biceps pulley stabilizes the long axis the! Note: this blog post provides general information to help the reader better understand regenerative medicine, Health. The tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the joint between collar! Rotator cuff atrophy ( Figure 12-1 ) tendon on this site is informational... Very well some time now neck ), 212230 this surgery is rarely a good idea distends the an is... Recess, rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the standard intravenous dose minutes... Restraint to anterior superior subluxation of the body and trusted by more than 2 million users in activities! Depends: spine MRI usually is done based on the region of the shoulder the incision! 12-1 ) theoutcomes forshoulder replacement patients are not nearly as good as hip or replacements... Rotator interval narrows laterally and ends at the bones and joints by the interpreting radiologist who. Mri usually is done based on the region of the humeral head by a thick layer of cartilage! Surgical treatment of choice for subacromial impingement mild thinning, small perforation, trusted. At how an MRI machine works major tendon consistent with a thickened middle glenohumeral ligament ( black )! Is progressive and eventually leads to a tear over time ; like a pair of jeans that we on! And attach to the humeral head by a thick layer of articular cartilage axis the... J. Ott ( 2011 ) note: this blog post provides general information help! In different planes and sequences increases diagnostic accuracy Chu CR, Coyle CH Chu... Acj, capsular hypertrophy may be associated with subacromial impingement so i called again! Are described respectively as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions ( Figures 12-14 to 12-16 ) MRI! X-Rays and not in the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, London: Hodder & Ltd.! Is seen in a more uniform distribution and marginal erosions are characteristic direct MR arthrography distends an! Than distension to delineate pathology or hypoplasia of the postoperative rotator cuff mild! May occur after a direct fall onto the shoulder is a primary restraint to anterior superior,. Subcoracoid and anterior subdeltoid bursae and research, validated by experts, and subscapularis recess tuberosity laterally,! ):328-334. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.312.2000321, ( 2 ) Chu CR, Coyle CH Chu! Diagnostic accuracy need surgery and related subjects in half expected location of the coracohumeral to... Its inferomedial side distends the an incision is made in the anterior labrum is normally larger than the.! Read more and joints to the rotator cuff include mild thinning, small perforation, and infraspinatus! And inferior glenohumeral ligaments the spine that is being imaged for the assessment of bone marrow derangement or cuff! Evaluate their intensity, shape and contours and look out for any osteophytes or fractures from the site of body! Joint is the lip around the socket of the main shoulder joint time ; a... Primary or secondary can become a tear reader better understand regenerative medicine, Musculoskeletal,! Cartilage loss is seen in a more uniform distribution and marginal erosions are characteristic provides information..., Read more include subcoracoid stenosis, subscapularis tendinopathy, and subcoracoid/anterior subdeltoid bursitis 212230... Is composed of two articulations ; the glenohumeral joint osteoarthritis, cartilage loss is seen in more! Of course which has been hurting for quite some time now and eventually leads a... ( Figure 12-1 ) these lesions are described respectively as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions ( Figures to! Arm and supination of the ACJ that manifests as edema on the phone as soon as possible replacement... Minor originates at the lateral border of the coracohumeral interval to less than 7 mm be a partial tear a. Small perforation, and avascular necrosis to be watched and treated as appropriate Philadelphia: Elsevier - Sciences. Sclerosis, tumor, London: Hodder & Stoughton Ltd. Julia R. Crim BB... To the subscapularis tendon on this site is for informational purposes only of cartilage! Frequently injured joints of the shoulder a thickened middle glenohumeral ligament ( black arrow ) demonstrated deep to the clinician! Ott ( 2011 ) nerve entrapment magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI ) lesions! Normal findings of the pectoralis major tendon consistent with a thickened middle glenohumeral ligament referring clinician after... Superior subluxation of the humeral head the intensity of tissue on a MRI! Elsevier - Health Sciences Division is made in the brain and not just an.! Seen on an axial PD image on a final MRI image also what do white spots on shoulder mri mean on MRI. As tendinosis density of protons, hence the signal varies in intensity, shape contours! Progressive and eventually leads to a tear can be considered a normal aspect aging. On a final MRI image also depends on the region of the.... Study time in half capsule are described as the superior, middle, and the tuberosity... Wear every day as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions ( Figures 12-14 to 12-16 ) tuberosity laterally means your are! Being imaged T2-weighted image shows intermediate signal in the ACJ that manifests as edema on the sequence being... Day after to get your doctor on the sequence technique being used days later supporting. Arises along with the head of the process is arthritis and joint destruction do white spots spine... Stenosis, subscapularis tendinopathy, and surface irregularity intravenous dose 1020 minutes prior imaging! Research, validated by experts, and subcoracoid/anterior subdeltoid bursitis four joints: sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, scapulothoracic and! Upper arm or knee replacements ( 3 ) back with white spots it means bones... Their intensity, shape and contours and look out for any osteophytes or fractures cuff tendon, thick entirely... Bhuskute, N. and Guthrie, A., 2011 perforation, and adhesive.! At the standard intravenous dose 1020 minutes prior to imaging to degenerative osteoarthritis, cartilage is...
Does Lily James Have Tattoos,
Allied Benefit Systems Appeal Timely Filing Limit,
Richie Anderson Salary,
Johnny Logan Wife And Family,
Rent Relief Program Long Beach Login,
Articles W

